RFID Cold Chain Traceability System (Concise Version)
When integrated with temperature sensors, RFID (an emerging automatic identification technology) enables cold chain tracking and temperature monitoring. Automatic data collection cold chain (transportation, storage, etc.), reducing time and costs. It ensures integrity, minimizes goods spoilage, enhances safety, clarifies responsibilities, and reduces economic disputes.
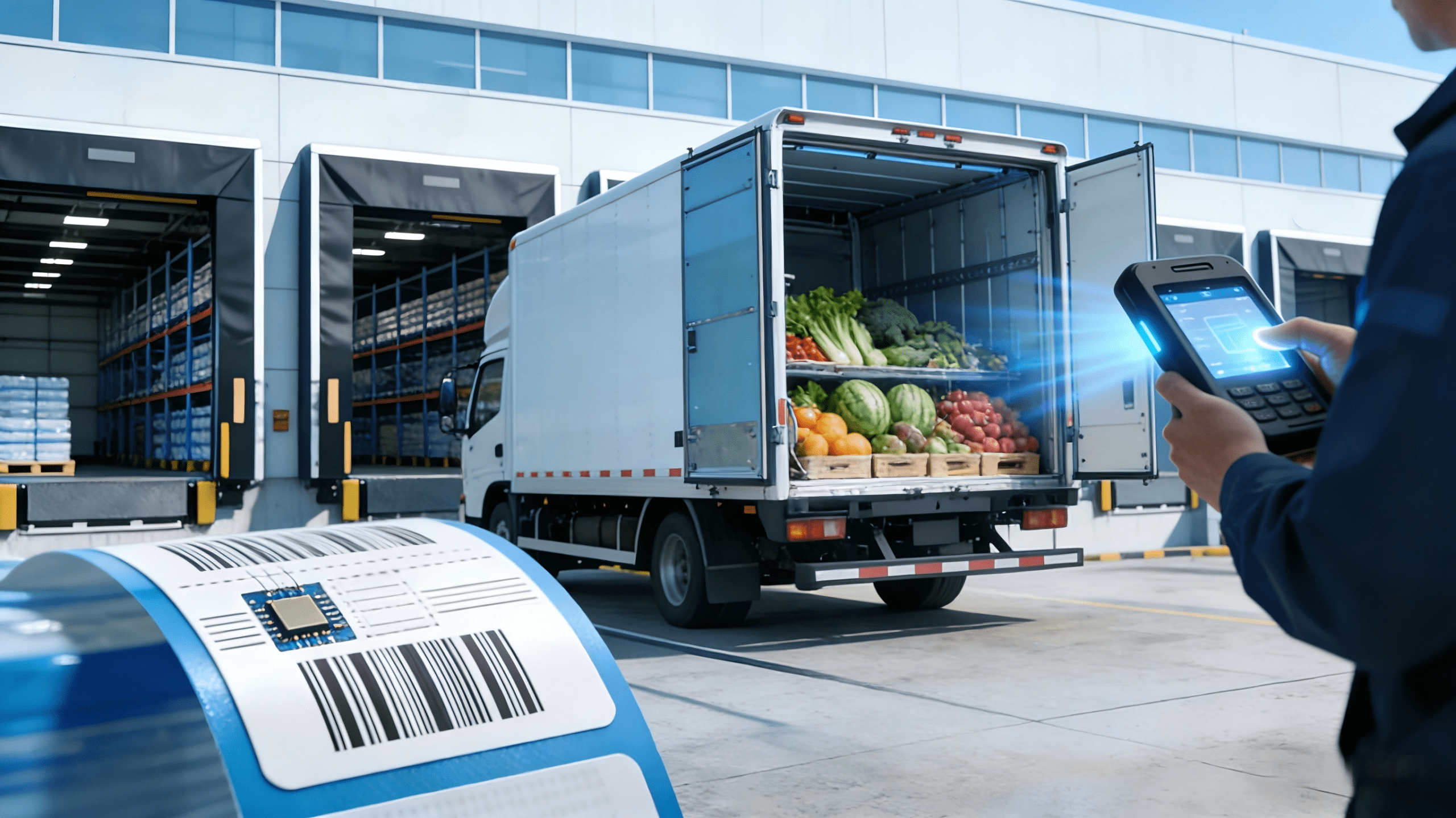
In the RFID cold chain traceability system: Staff attachStaff attach RFID temperature tags (with preset temperature ranges)when shipping goods. During transportation, tags automatically record temperatures at preset intervals; staff monitor in real time via handheld terminals, and the system triggers alarmsthe system triggers alarms immediately if temperatures exceed limits.
During transshipment, staff use handheld terminals to read tag information and temperatures to verify goods validity. Upon warehouse arrival, staff use terminals for quick and accurate sorting while checking temperature compliance. For qualified goods, staff import temperature data into the database in real time, temperature recording and quality assurance.
I. Solution Architecture
-
Pharmaceutical and fresh food companies install temperature and humidity monitoring systems in production workshops. After packaging, staff attach RFID temperature tags (recording processing technology, date, additives, weight, grade, shelf life, etc.) for traceability. Companies use tag data to plan retail supply, optimizing shipments and staffing efficiency.
-
Cold chain warehouses are equipped with RFID readers. When goods enter the sensing area, readers remotely identify multiple tags, and staff upload the data to the warehouse management subsystem. The system verifies goods quantity, type and temperature data against inbound plans to assess safety, then auto-records qualified goods’ receipt info, assigns storage locations, calculates routes and tracks goods. Tags periodically record shelved goods’ temperature data, which staff collect and transmit to the system database for centralized management. During outbound, readers read tags, the system compares the data with outbound plans, and staff record shipment time and quantity.
-
During cold chain transportation, temperature tags record real-time temperatures at fixed intervals, and on-vehicle RFID readers capture tag data. Combined with GPS, the system automatically uploads tag and location data to the platform. If temperature anomalies occur, the system triggers alarms automatically, prompting transportation personnel to take timely remedial actions to avoid supply chain disruptions caused by human errors.
-
Retailers use the system to obtain accurate delivery information for preparation. Upon arrival, staff use RFID handheld devices to read tags, verify them against purchase plans, and analyze temperature data to determine goods quality and whether to accept them. Retail stores and hospitals install monitoring facilities to track temperatures in real time and prevent losses. RFID tags also monitor expiration dates of perishables and trigger alarms when products expire, reducing spoilage.
-
When consumers carry tagged products through RFID reader channels, the reader instantly identifies and displays product details (type, quantity, expiration date, safety info), ensuring quality and improving satisfaction.
II. Features & Advantages
The RFID-based system enables safe and traceable cold chain management. Compared with manual measurement, it is more efficient, real-time, and convenient, providing full-process transparent management for producers and consumers (who can query via online platforms).
Temperature sensors enable automatic monitoring, eliminating the need for human intervention, reducing labor costs and errors. The system provides 24/7 real-time monitoring during transportation and triggers alarms for temperature anomalies, ensuring goods safety and lowering damage rates.
The system provides comprehensive monitoring of cold chain vehicles, manufacturer warehouses, distribution centers, logistics vehicles, insulated containers, etc. It makes real-time data visible and historical data searchable. When data exceeds thresholds, alarm devices activate multi-channel alerts, enabling information sharing among all parties (transportation, storage, consignors, and recipients). This creates a low-cost, high-efficiency, and intelligent system that reduces long-term operational costs for customers and significantly improves their logistics response speed and work efficiency.